| Things we must have to survive. | Needs |
| The next best alternative forgone. | Opportunity Cost |
| Things we would like to have | Wants |
| Because of scarcity we have to make | Choices |
| Things we have to pay for | Economic Goods |
| Things we don't have to pay for | Non Economic Goods |
| Examples of values include……. | Honesty, Integrity, Consideration of others, loyalty. |
| Examples of limited means | Time, income and skills. |
| Wants are unlimited but means are | Limited. |
| Because of unlimited wants but limited means we have | Scarcity |
| People are naturally greedy and so we have | Unlimited Wants |
| Things people hold to be important | Values |
| A want is different to a demand because to have a demand you have to be | Able to buy it. |
| All other factors remaining unchanged | Ceteris Paribus |
| Products that are used together / in conjunction with each other | Complements |
| A table showing how much people are willing to buy at a range of prices. | Demand Schedule |
| How much of a commodity a consumer is both willing and able to buy at a given price. | Demand |
| An increase in income will cause a decrease in demand for this type of good. | Inferior |
| A change in price will cause a change in the. | Quantity demanded. |
| Ceterus Paribus | All other factors remain unchanged. |
| A change in anything other than price will cause the demand curve to... | Shift and there will be a change in demand. |
| A change in Ceteris Paribus will cause the demand curve to. | Shift |
| The horizontal summation of each individual consumers demand at each price. | Market demand. |
| The only thing that will cause a change in quantity demanded and a movement along the demand curve. | A change in price. |
| An increase in price will lead to a…. | Decrease in the QUANTITY demanded and a movement along the demand curve. |
| A decrease in price will lead to ... | An increase in the QUANTITY demanded and a movement along the demand curve. |
| An increase in income will mean people will buy more because they can now…. | Afford to. |
| A decrease in income tax will cause the demand curve to.. | Shift right and demand will increase. |
| A decrease in the price of a substitute will cause the demand curve to. | Shift left and demand will decrease. |
| Substitute good. | A good used in place / instead of another good. |
| For a person to have a demand they must be both. | WILLING and ABLE to buy the good. |
| The Law of Demand | An increase in price will lead to a decrease in the quantity demanded. Ceterus Paribus. |
| If the price of a complement decreases then demand for the original good will do what? | Increase and the demand curve will shift to the right. |
| The total average spending by households. | Aggregate household spending. |
| As income increases the percentage of income spent on necessities will…. | Fall - the amount of money spent may stay the same or increase slightly, but as a percentage of income it will decrease. |
| Because of unlimited wants but limited means we have to make choices which involves making… | Decisions. |
| Factors that will shift the demand curve to the right and increase demand. | Increase in income, increase in the price of a substitute, decrease in the price of a complement, good advertising, decrease in income tax. |
| As income increases people spend more on. | Luxury goods. They can also afford to save more. |
| People with low incomes will spend most of their money on.. | Basic needs, basic necessities. |
| Examples of basic necessities include... | Clothing, basic food items, shelter. |
| Income not spent. | Savings. |
| Factors that will shift the demand curve left. | Decrease in income, decrease in the price of a substitute, increase in the price of a complement, increase in income tax. |
| Income after tax. | Disposable income. |
| The main examples of limited means are. | Time, income, skills and sometimes whanau / family. |
| Disposable income. | Income after tax. |
| An increase in the price of this will lead to a decrease in demand for the original good. | Complement |
| An increase in the price of this will lead to an increase in demand for the original good. | Substitute |
| If the price of a substitute decreases then... | Demand for the original good will decrease. |
| If the price of a complement increases then... | Demand for the original good will decrease. |
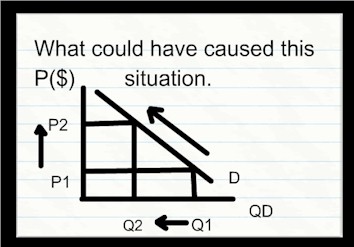 | An increase in price which has lead to a decrease in the QUANTITY demanded. |
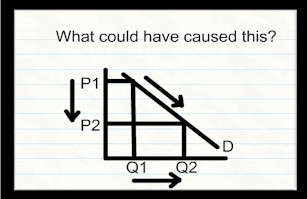 | A decrease in price which has lead to an increase in the QUANTITY demanded. |
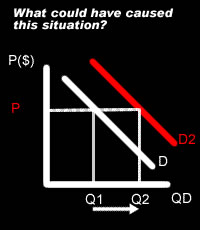 | An increase in income, good advertisiing, increase in the price of a substitute, a decrease in the price of a complement, a decrease in income tax. |
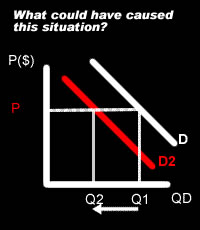 | A decrease in income, decrease in the price of a substitute, an increase in the price of a complement, an increase in income tax. |
| All Cards Revised. | Remaining Cards |







