INTERACTION OF FIRMS IN THE MARKET
| PRICE COMPETITION | ||
| Producers use this strategy to try and undercut the
competition and increase sales. By reducing their price producers are trying to increase the quantity demanded for their product and decrease the demand for their competitor�s product. |
||
Price competition involves the firm in some way
reducing its price, and may include.
|
||
| Price competition may lead to
price wars where two or
more firms try to undercut each other. This may lead to a loss in
profits and eventually one of the firms closing down. Recent price wars
can be seen in the airline industry. Larger firms such as the Warehouse, are able to take advantage of economies of scale such as bulk buying, marketing economies etc. and undercut smaller firms eliminating them. There are often a lot of arguments about �big box� stores that often eliminate smaller firms when they come to a town. |
||
Advantages of
price competition include:
|
Disadvantages of
price competition include:
|
|
| NON PRICE COMPETITION | ||
| Non price competition
allows firms to compete without reducing their prices. This involves encouraging consumers to buy a good by making it appear different or better to the other products.
|
||
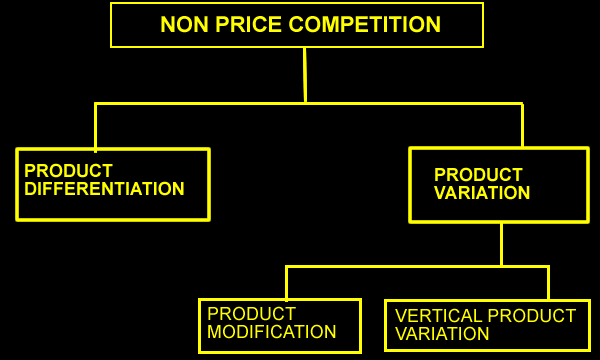
| THE MAIN FORMS OF NON-PRICE COMPETITION ARE... | ||
 |
||
Product differentiation
includes
|
||
| PRODUCT
VARIATION Product variation is where firms give their product real variations to try and get consumers to buy their product. PRODUCT MODIFICATION Producers give their products real differences such as airbags in cars, better body designs, raspberry coke etc. The modificatications may draw customers away from their competitors. |
VERTICAL PRODUCT VARIATION To make their product appeal to a wider range of income levels, some producers may introduce a number of different models of the same product. e.g. Car manufactures may have the economy model, GTI model, station wagon model, sports model with different engine sizes or extra features for the more expensive models, but the body design general aspects are still the same. |
|
| ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NON-PRICE COMPETITION. | ||
Advantages to Suppliers
|
 |
|
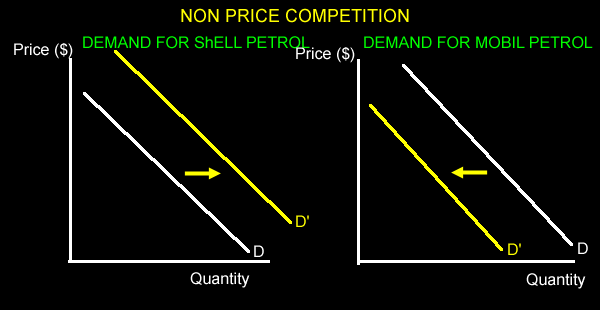
| Non price competition will increase the demand for the product by shifting the demand curve to the right. Consumers are more willing to buy more of the good. This reduces the demand for competitiors products and so their demand curve shifts to the left. | ||
| Disadvantages to Suppliers
|
||
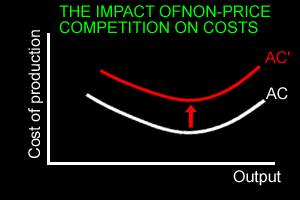 |
Non price competition will increase the average cost of production for the product as more is spent on advertising, competitions etc. | |
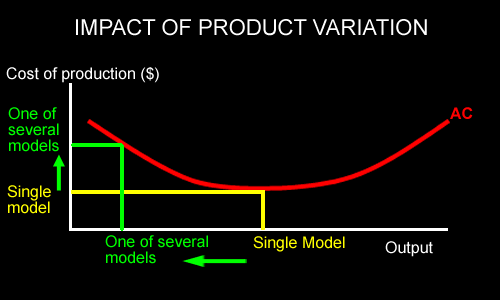
| Vertical product variation leads to increased costs of production for each model of products as less able to take advantage of economies of scale. |
|
|
| ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTGES OF NON PRICE COMPETITION |
||
ADVANTAGES TO CONSUMERS
|
DISADVANTAGES TO CONSUMERS
|
|