OBJECTIVES:
-
Classify human, capital and
natural resources.
-
distinguish between
renewable and non-renewable resources.
-
identify resource use for a
particular production process.
-
Explain the characteristics
of the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors, and the importance
of each to the economy.
|
| Production
is the combining of resources
to create a good or service.
A resource is the input
into the production process. The resources used in the production process
are referred to as the factors of production. |
| The
factors of production |
| These
are |
- Land
- anything from the natural environment.
- Labour
- human resources.
- Capital
- Man made good used to produce other goods.
- Entrepreneurship
- a human resource that organises the factors of production.
|
| Land can
be defined as any natural resource. |
| Land
can be divided into two types of resources. |
| Renewable
Resource any
resource that can be replaced or replenished within our life time.
As long as it is used sustainably it will not run out. |
|
Examples include - sheep, fish, wind, water, pine trees. |
| Non-Renewable Resource any
resource that is depletable - it cannot be replaced or regenerated within
our life time. |
|
Examples include - oil, coal, trees that take a long time to grow such as
Kauri trees. |
| Labour
is any human resource that is
used in the production process. The total number of people who are able to
work is the work force. |
| Capital
- this is a man made resource used to produce
other goods. In Economics the buying of capital is called
investment.
Capital
can be divided into two types |
| Productive
Capital is the machinery or
factory, any capital which is not used up in the productive process. |
| Circulating
Capital this is the semi
finished goods that go into the productive process for example in making a
car we need: glass, rubber and steel. These are all resources that have
been processed and are used up in the production process - they can't be
used to create any more goods and services. This is also known as
intermediate goods. |
| A
special feature of capital goods is that they
depreciate - they lose value over time. |
| What
resources would have been used to make the cake below? Use the resource
list next to the picture to complete the table. |
 |
Eggs,
Flour, bakery owner, water, butter, mixer, cocoa, oil, water,
baker, factory, shop assistant, bowls, spoons, oven, sugar and milk.
|
|
| |
| |
|
Resources are combined to create a good or
service. How the resources are combined will depend upon a number of
factors. These include: |
- The cost of the resource.
- The availability of the resource
|
|
Labour intensive
production is when
relatively more labour than capital is used in the production process.
Industries in the service sector such as shops and restaurants use labour
intensive production. Countries with cheaper labour also tend to use labour
intensive methods of production. |
|
Capital intensive production
is when more capital than labour is used in the production process such as
car manufacturing. Capital intensive production is often used in the
secondary sector where machines are able to carry out many of the tasks. The
advantages of machinery is that it can work 24 hours a day, can do dangerous
or monotonous tasks faster and more accurately and where labour is
relatively expensive it allows for cheaper methods of production. |
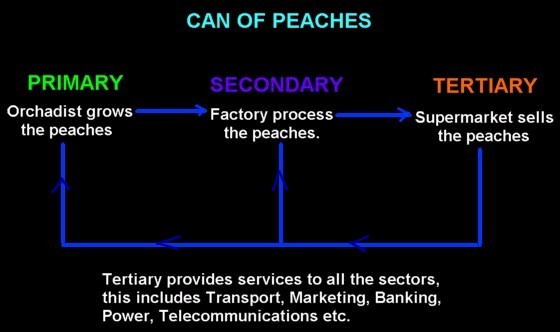
| Primary Sector |
| The primary sector extracts raw materials from the land. |
| Any process which involves the extraction or harvesting of raw materials from the natural environment is part of the Primary Sector. |
| Sheep farming uses land and sheep to produce the goods of wool and sheep meat - these are extracted from the natural environment. |
| The fishing industry harvests fish from New Zealand waters. |
| Mining produces coal, oil, natural gas. |
| Forestry produces timber. |
| The primary sector produces half of New Zealand's exports. |
|
|
|
|
Secondary Sector |
| Industries in this sector take raw materials from the primary sector and process them into finished or semi-finished goods. Firms in this sector take an input (usually a raw material from the primary sector) process it and then produce an output (either a finished good or a semi-finished good). |
Secondary production includes -
- Manufacturing
- Processing
- Assembling
- Refining
|
| |
Tertiary Sector |
This sector provides services to all sectors and consumers. The tertiary sector includes services such as transport and education. Examples of some of the services a typical business would require are
- communications (telephone, fax, internet etc)
- transport (cars, buses, trucks planes etc.)
- utilities (electricity, gas etc).
- financial services (banks etc)
- personal services (doctor etc.)
|
Interdependence of the Sectors |
| Each sector depends on the other sectors i.e. they are interdependent. |
| |
| Primary and secondary depend on each other: one to supply raw materials and the other to use them for producing finished goods. |
| The tertiary sector provides services to both of the other sectors and in turn the tertiary sector relies on the Primary and Secondary sectors for their products and to use their services for income. |
| Tertiary provides other services to all firms, e.g. advertising, health, education, transport of goods, banking, power, accounting services. |
| Case Study |
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
|
 |
| |
|
|