CHANGES IN DEMAND AND SUPPLY
An INCREASE IN DEMAND will cause the demand curve to shift right. This will cause a SHORTAGE at the current market price. Consumers will be unable to buy all the products they want at the old equilibrium price. Producers will increase the price because they will be able to get more profit. As the price increases the quantity supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases. The market will go to the new equilibrium price and quantity. In the example the price for DVD's will increase from $30 to $35 and the QS of DVD's will increase from
|
 |
An INCREASE IN SUPPLY will cause the supply curve to shift to the right. This will cause a SURPLUS at the current market price. Producers will be unable to sell all of the products at this price. Producers will lower the price to sell their excess stock. As the price decreases the quantity supplied decreases and the quantity demanded increases. The market will go to the newequilibrium price and quantity. In the eqample the price for DVD's will fall from $35 to $30 and the QS of DVD's will decrease from 45 000 to 30 000 and the QD will increase from 20 000 to 30 000 - going to the new equilibrium price and quantity. |
 |
THE EFFECTS OF AN INCREASE IN SUPPLY ON CONSUMER SURPLUS.When there is an increase in SUPPLY there will be an increase in both consumer and producer surplus'. As the supply curve shifts to the right, some of the producer surplus is transferred to the consumer, but both are better off. With supply shifting to S2 the quantity supplied shifts to QE2 and the price changes to Pe2 causing an increase in surplus for both consumers and producers. Producer surplus before the increase was the area in blue, after the increase in supply to S2, the new surplus is the area in pink. Consumer surplus before the increase in supply was the area in green and after the increase is now the area in green, blue and gray. |
 |
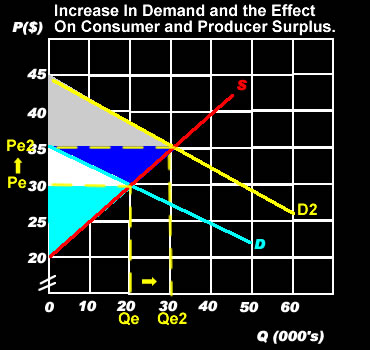
THE EFFECTS OF AN INCREASE IN DEMAND ON CONSUMER SURPLUS.When there is an increase in DEMAND there will be an increase in both consumer and producer surplus'. As the demand curve shifts to the right, some of the consumer surplus is transferred to the producer, but both are better off. With demand shifting to D2 the quantity demanded shifts to Qe2 and the price changes to Pe2 causing an increase in surplus for both consumers and producers. Producer surplus before the increase was the area in light blue, after the increase in demand to D2, the new surplus are the areas in white, blue and light blue. Consumer surplus before the increase in supply was the area in white and after the increase is now the area in gray.
|
 |