DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF LABOUR
OBJECTIVES:
The concept of the demand and supply of labour.
The main determinants of demand for labour.
The influences on supply of labour.
The role of the labour market is to
To reconcile supply and demand.
To direct available labour to the highest value uses.
To provide incentives for improving its quality through training and skill development.
Failure in the labour market is generally reflected in unemployment and the persistent mismatching of skills to jobs.
THE DEMAND FOR LABOUR
The demand for labour is a derived demand this means that there is no direct demand for labour, it is influenced by the demand for the products the workers produce.
 |
The diagram shows the demand for labour.
There is a negative relationship between wage rates and the quantity of labour demanded. As wages increases firms will demand less labour as they will either cut production or look at alternative methods of production.
W stands for the wage rate. Wages are the price of labour or dollars paid per hour.
Q stands for the quantity of labour demanded by producers.
Any change in the wage rate causes a movement along the demand curve for labour.
An decrease in wages will result in an increase in the quantity demanded for labour.
|
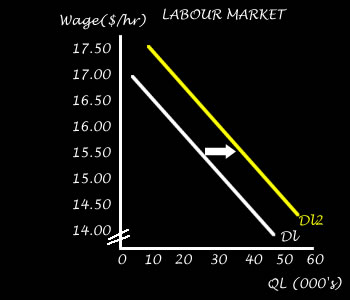 |
Factors that will cause an increase in the demand for labour (a shift to the right of the demand curve).
- increase in the demand for a product.
- increase in productivity.
- new technology that increases worker productivity.
- increase in exports.
- growth in the economy.
- anything that will cause Aggregate Demand to increase.
|
 |
Factors that will cause a decrease in the demand for labour (a shift to the left of the demand curve).
- decrease in the demand for a product.
- decrease in productivity.
- new technology that replaces workers - more capital intensive production.
- decrease in exports.
- increase in imports.
- a recession.
- anything that will cause Aggregate Demand to decrease.
|
THE SUPPLY OF LABOUR.
There is only a certain number of people that are willing and able to supply their labour at a given wage rate. The number of people able to be employed is also restricted by such things as the working age population, any employment laws, social attitudes to employment etc.
The participation rate indicates the percentage of the working age population participating in the labour force.
There is a positive relationship between the wage rate and the number of workers willing to supply their labour to the market.
People are likely to sacrifice leisure time (the opportunity cost of working) if the wage rate increases.
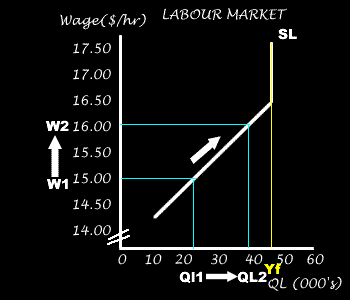 |
As wages increases more workers are willing to supply their services to the market and so the quantity of Labour supplied will increase.
Eventually once all workers are employed (at Yf) then additional increases in the wage rate cannot increase the quantity supplied. And so the supply curve becomes vertical.
Any change in the wage rate will cause a movement along the curve.
An increase in the wage rate will cause an increase in the quantity supplied of labour.
|
 |
An increase in the supply of labour can be caused by...
-Net migration gain, immigration
-Decrease in school leaving age.
-Increase in retirement age.
-Decrease in nthe school leaving age.
-Decrease in welfare benefits.
-Increased participation.
An increase in the supply of labour will cause the supply curve to shift right.
|
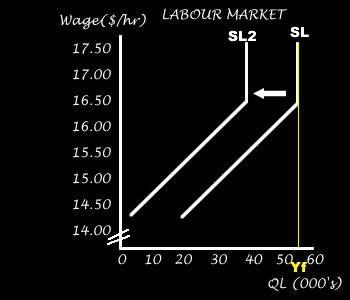 |
A decrease in the supply of labour can be caused by...
-Net migration loss.
-Increase in school leaving age.
-Decrease in retirement age.
-INcrease in school leaving age.
- Increase in welfare benefits.
- Decreased participation.
A decrease in the supply of labour will cause the supply curve to shift left.
|





