OBJECTIVES:
ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF UNEMPLOYMENT.
 |
LOST PRODUCTION The opportunity cost of unemployment is lost production. If the economy moves from point A to B then there are more unemployed resources and so economic efficiency falls, leading to a reduction in a countries competitiveness. |
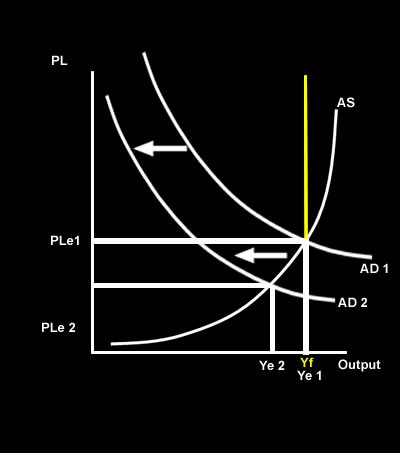 |
REDUCED DEMAND Reduced income in the economy due to unemployment leads to a reduction in consumption of goods and services. Reduced consumption reduces AD leading to a further negative impact on the economy. Reduced consumption due to unemployment will lead to a fall in Aggregate Demand – in this case increasing the recessionary gap. The economy is further away from full employment leading to falling incomes and consumption – production falls, tax intake falls and the economy may enter a recession. |
REDUCED TAX INTAKE
SOCIAL WELFARE PAYMENTS INCREASE
LOSS OF SKILLS- The longer someone is unemployed the less likely it is that they will retain important work skills.
REGIONAL STAGNATION- The loss of key industries in small towns or already depressed areas can have severe effects.
SOCIAL EFFECTS OF UNEMPLOYMENT
SOCIAL STRESS
The human effects of unemployment include
Periods of unemployment can break up an individuals work record and this can make finding another job difficult.
Poverty: high unemployment can lead to people being discouraged and giving up trying to find work. This will lead to increased poverty and continued unemployment, especially for some sections of society.
Reduced family income is likely to mean
There has been some link shown between an increase in suicide rates and unemployment.
CRIME
There does seem to be a link between crime and unemployment but crime while connected is affected by a number of factors.
INEQUALITY
The effects of unemployment are not spread evenly through the economy. Some ethnic groups have a higher rate of unemployment than other groups.
Older people also find it harder to find a job, especially those over 40.
People trapped in long term unemployment Can give up, suffer a loss in skills, even simple ones, leading to a reduction in their employability.
MIGRATION
Increased emigration.
When people become unemployed they have the option of leaving, this can create a number of problems. These include
THE IMPACT OF EMPLOYMENT ON DIFFERENT GROUPS
EFFECT ON HOUSEHOLDS
|
EFFECT ON PRODUCERS |