EMPLOYMENT OBJECTIVES:
Working age population - the resident population who are 15 years and older.
The labour force- the part of the total population willing and able to work; most will have jobs, but some will not.
Full time labour force � those working over 30 hours a week or those who are unemployed and seeking full time work.
Part time labour force � those working 1 -29 hours per working or who are unemployed and seeking part time work.
The participation rate - is defined as the labor force divided by the size of the civilian non-institutional population (people in places such as prisons). Individuals who are out of the labour force fall into one of a number of categories. They include
Labour Supply
When the real wage increases, it affects the supply of labor in two ways.
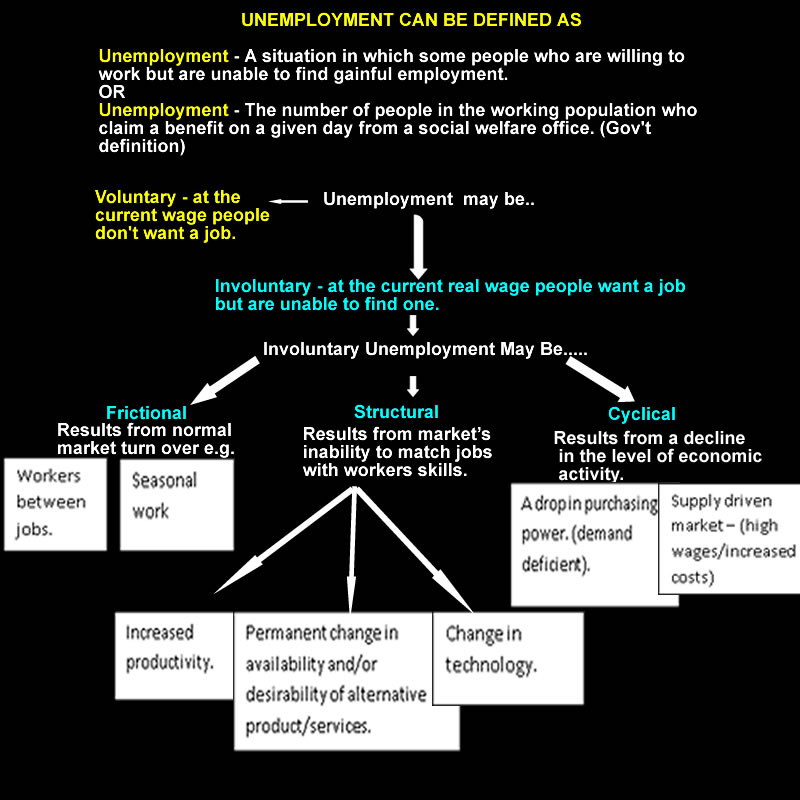
Natural Rate of Unemployment.
Full employment in the past has been 1-2% of unemployment.
Some would argue in more recent times that this rate should be higher. Between 1961 and 1971 the natural unemployment rate was less than one per cent of the labour force.
It is now suggested to be 3 to 5%. It is an acceptable rate of unemployment because there will always be a number of workers between jobs or temporarily between jobs or temporarily unemployed.
What is a natural rate of unemployment? This is the rate considered to be impossible to go below.
UNEMPLOYMENT AND THE PPF AND AD/AS MODEL